1. Setup network security to allow Kafka ports (9092)
2. Create and Attach EBS volumes to EC2 Instances
(to have a separate drive for Kafka operations)
3. Format the newly attached EBS volumes as XFS
(recommended file system for Kafka as per documentation - requires less tuning)
4. Make suer the volume stays mapped on reboot
5. Apply on all machines
#!/bin/bash
# execute commands as root
sudo su
# Attach the EBS volume in the console, then
# view available disks
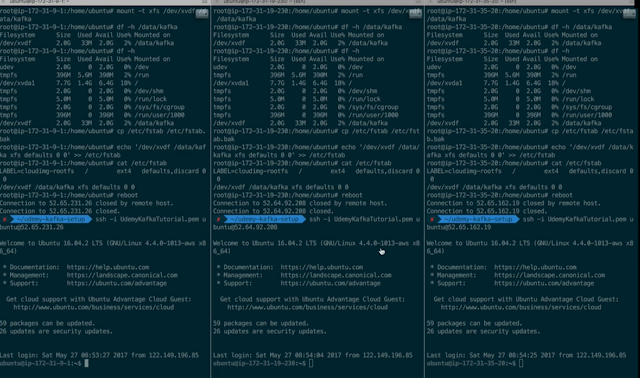
lsblk
# we verify the disk is empty - should return "data"
file -s /dev/xvdf
# Note on Kafka: it's better to format volumes as xfs:
# https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#filesystems
# Install packages to mount as xfs
apt-get install -y xfsprogs
# create a partition
fdisk /dev/xvdf
# format as xfs
mkfs.xfs -f /dev/xvdf
# create kafka directory
mkdir /data/kafka
# mount volume
mount -t xfs /dev/xvdf /data/kafka
# add permissions to kafka directory
chown -R ubuntu:ubuntu /data/kafka
# check it's working
df -h /data/kafka
# EBS Automount On Reboot
cp /etc/fstab /etc/fstab.bak # backup
echo '/dev/xvdf /data/kafka xfs defaults 0 0' >> /etc/fstab
# reboot to test actions
reboot
sudo service zookeeper start




댓글 없음:
댓글 쓰기